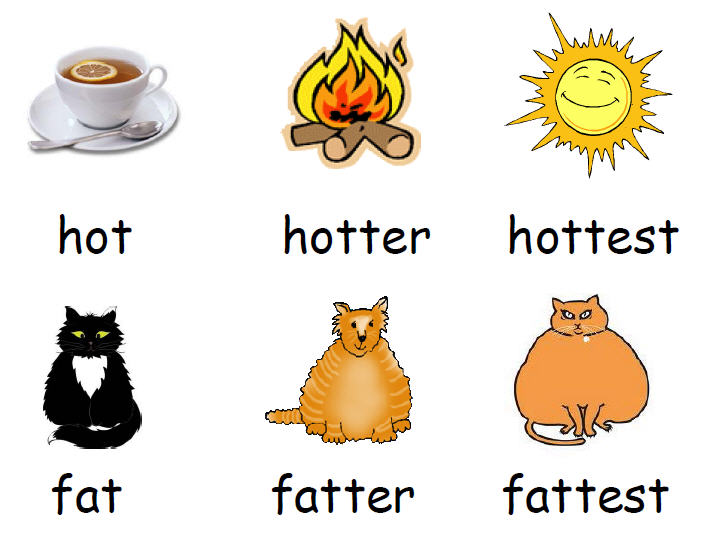
Vamos descobrir quais são?
Antes de compreender quando utilizar o "how much" ou "how many" e descobrir quais são contáveis (countable) e quais são incontáveis (uncountable) vamos nos atentar ao significado das palavras:
Much significa muito:
Note, em português nós dizemos, muito café, muito arroz, muito açúcar, então, em inglês vamos dizer, much coffee, much rice, much sugar...
Many significa muitos:
Prestaram atenção no "s"? Em português temos, muitos livros, muitos amigos, muitas canetas... Ou seja, seguindo a lógica, em inglês fica, many books, many friends, many pens...
Conseguiram assimilar?

How much x How many
A lógica praticamente é a mesma!
How much significa quanto para "coisas" incontáveis e How many para "coisas" contáveis.
Vejamos um exemplo:
How many books did you buy?
How much coffee should you drink?
Conseguiu compreender?
Então para facilitar sua vida, separamos uma listinha com alguns substantivos contáveis e incontáveis considerados na Língua Inglesa:
Countable nouns (substantivos contáveis) são aqueles que têm tanto a forma singular quanto plural:
cat - cats
table - tables
book - books
newspaper - newspapers
pen - pens
Uncountable nouns (substantivos incontáveis) é o nome que damos para as coisas que só existem no plural.
water
coffee
milk
sugar
cheese
rice
butter
oxygen
wine
beer
luck
salt
money
music
ink
air
snow
evidence
weather
jewerly
proof
housework
permision
eletricity
Para facilitar o entendimento:
- Não podemos dizer one water, three salts, two moneys, five musics.
- Os substantivos incontáveis nunca são precedidos pelos artigos indefinidos a/an:
a water
a money
a salt
an ink
- Os substantivos incontáveis frequentemente indicam:
- substância - food (comida), iron (ferro), water (água)
- atividades - help (ajuda), travel (viagem), work (trabalho)
- qualidades humanas - courage (coragem), cruelty (crueldade), honesty (honestidade)
- ideias abstratas - beauty (beleza), freedom (liberdade), life (vida), luck (sorte), time (tempo)
Atenção: Muitas vezes falamos certas coisas no plural: duas águas, três cafés, seis cervejas. Mas, as pessoas esquecem que nesses casos, não contamos o líquido. O que contamos é a quantidade que compramos ou tomamos. Logo, é preciso colocar em contexto para entender a diferença. Ou seja, quando alguém diz “traz duas águas pra mim”, o que ela quer dizer é “traz duas garrafas de água pra mim”.
No dia a dia, nós cortamos a sentença, pois já está claro no contexto o que queremos dizer. Se você entender isso, certamente compreenderá a ideia de countable and uncountable nouns.
Outros exemplos:
Ela tomou seis cafés. (Ela tomou seis xícaras de café.)
Em inglês informal isso também é possível. Então, você poderá ouvir alguém dizer algo como “I want two beers” e “she had six coffees”. Mas, nesses casos, lembre-se que a pessoa estará se referindo à quantidade (dos recipientes) e não ao liquido em si.
Há mais palavras usadas assim, separamos as mais comuns
information (informação)
slang (gíria)
baggage e luggage (bagagem),
furniture (mobília, móveis)
advice (conselho)
fruit (fruta)
Esperamos que esse post tenha te ajudado a compreender as diferenças.
See you next one!